With the wane of physical media which is extremely limited, Digital media is exponentially becoming the dominant way we listen to music, watch videos, and view still images.
And there is no single file format that takes care of it all. (How unfortunate).
Hence it becomes important for us to understand media type and file formats. So that you don’t encounter with an instance where your device or browser says “unsupported file format”.
There is a lot to cover in this article, so let’s begin without any further delay.
Media type & File format:
Media type was previously known as MIME (Multipurpose internet mail extensions.) It is a two-part identifier for the file format, first is the type of media and second is the type of extension. ex- video.mp4
IANA is an official authority for standardization and publication of these classifications. You can check out the IANA website for media type here: https://www.iana.org/assignments/media-types/media-types.xhtml
You can get to know about media type naming, registration trees, suffix, mailcap, and mime type on Wikipedia.
Digital media files are encoded so that computer programs or apps can read and work with it.
<
video width="320" height="240" controls>
<source src="movie.mp4" type="video/mp4">
<source src="movie.ogg" type="video/ogg">
Your browser does not support the video tag.
</video>
<
audio controls>
<source src="horse.ogg" type="audio/ogg">
<source src="horse.mp3" type="audio/mpeg">
Your browser does not support the audio tag.
</audio>
Now have a look at the table below, which browser supports which file format for video and audio.
Video:
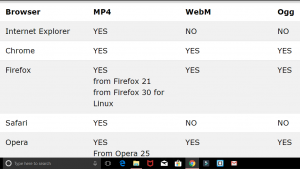
Audio:
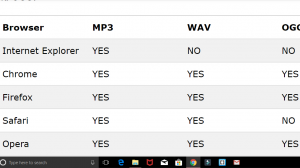
Get familiar with a few formats:
- MP4 = MPEG 4 files with H264 video codec and AAC audio codec
- WebM = WebM files with VP8 video codec and Vorbis audio codec
- Ogg = Ogg files with Theora video codec and Vorbis audio codec
Codec:
Many times we have to convert the file format so that it can be played by programs other than the software for which it was originally created. This is called “Coder-decoder” OR codec for short.
Converting the file format so that it can be played by another program, or by an incompatible device is called “transcoding”.
Commonly Used Digital Media File Formats:
- Photo File Formats: JPEG, GIF, PNG, TIFF, BMP
- Music File Formats: AAC (WebM), MP3, WAV, WMA, DOLBY DIGITAL, DTS
- Other music file formats you may have access to AIFF, ASF, FLAC, ADPCM, DSD, LPCM, OGG
- Video File Formats: MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4 (mp4), AVI, MOV, AVCHD, H.264, and H.265.
- Other video formats you may have access to DivX and DivX HD, Xvid HD, MKV, RMVB, WMV9, TS/TP/M2T
Don’t worry if all of this seemed like an alien language to you, I have a solution for you.
Media playback:
You can install or take help of some application and software that will play your media file regardless of the file format that your device or browser supports. Here are a few to name.
- Mx player
- VLC Media player
- All connect
- DG UPNP
- Plex
- Twonky
- Roku Media
- Airplay DLNA receiver
I hope that this article was helpful to you. You can check out other articles as well.
Thank You.
